Overview of Real-Time Jobs
The DataArts Migration module of DataArts Studio provides real-time data synchronization, which replicates data from one source to another without affecting data consistency. This function enables real-time flow of key service data.
- Typical scenarios: real-time analysis, report systems, and data warehouse environments
- Characteristics: Real-time synchronization meets requirements such as many-to-one and one-to-many synchronization, dynamic addition and deletion of synchronization tables, and synchronization between tables with different names.
Figure 1 How real-time synchronization works
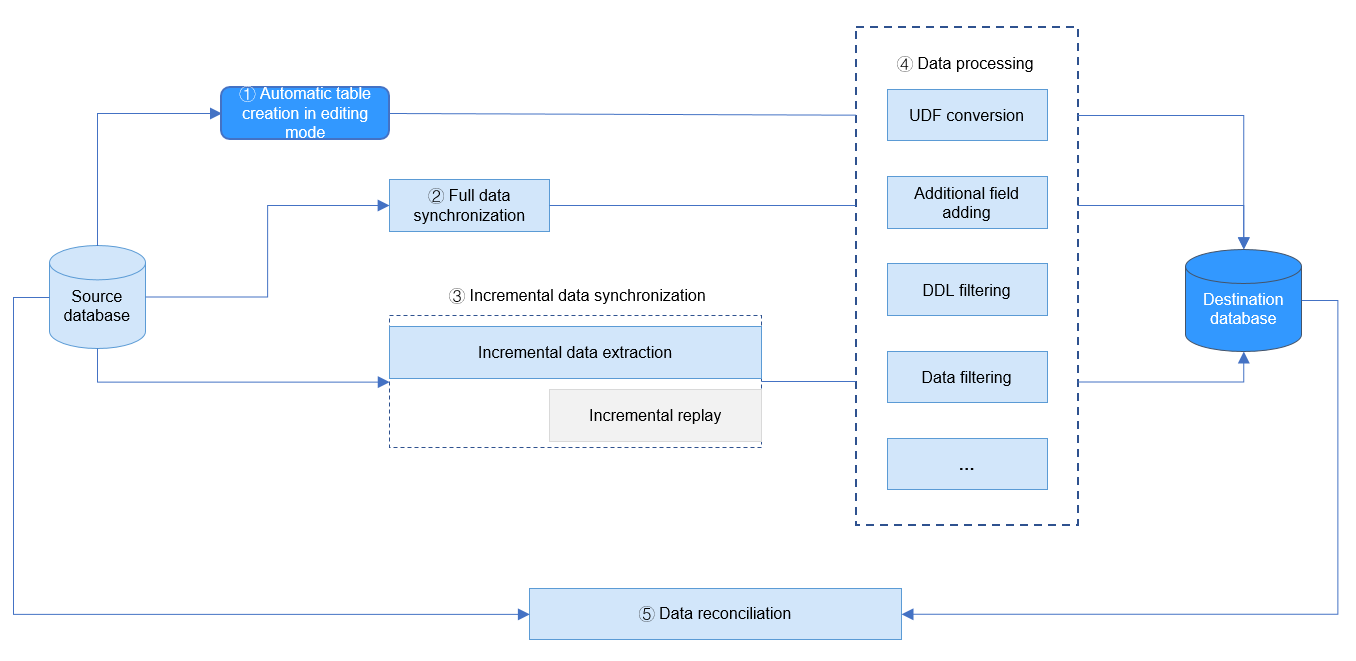
Functions
Real-time migration jobs support real-time data synchronization between a wide range of data sources in various scenarios. You can synchronize multiple database tables in full or incremental mode at a time. The following figure shows the detailed functions.
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Data synchronization between sources |
Various types of data sources are supported. You can combine multiple input and output data sources to form a synchronization link. For details, see Supported Data Sources. |
|
Data synchronization in multiple scenarios |
Real-time incremental data synchronization is supported for a table, an entire database, and database and table shards.
|
|
Real-time synchronization task configuration |
Real-time data synchronization can be implemented through simple visualized configuration.
|
|
Real-time synchronization task O&M |
Recovering tasks upon exceptions, dynamically adding or deleting tables, configuring alarms, and viewing and exporting task logs |
Synchronization Scenarios
DataArts Migration supports synchronization scenarios of multiple topology types. You can plan synchronization based on your requirements.
- Single table synchronization
A table in an instance can be synchronized to another instance.
The following links are supported:
to Hudi
Figure 2 Single table synchronization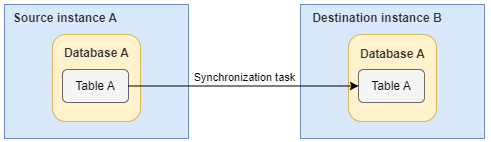
- Entire database synchronization
Multiple tables in multiple databases in an instance can be synchronized to another instance in real time. A task can synchronize a maximum of 200 tables.
The following links are supported:
- MySQL to MRS Hudi, MySQL to GaussDB(DWS), and MySQL to Kafka
- SQL Server to MRS Hudi and SQL Server to GaussDB(DWS)
- PostgreSQL to GaussDB(DWS), PostgreSQL to MRS Hudi, and PostgreSQL to
- Oracle to GaussDB(DWS), Oracle to MRS Hudi, and Oracle to
- GaussDB Centralized/Distributed to GaussDB(DWS), GaussDB Centralized/Distributed to MRS Hudi, and GaussDB Centralized/Distributed to
Figure 3 Entire database synchronization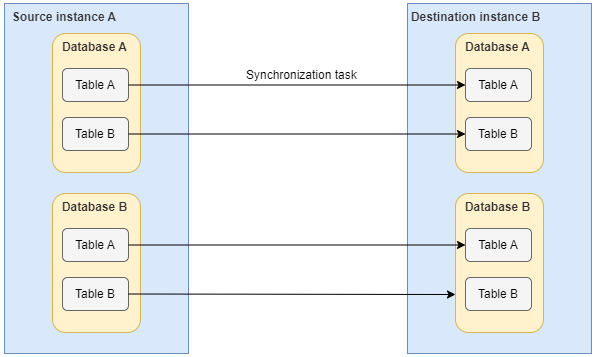
- Database and table shard synchronization
Multiple table shards of multiple databases in multiple instances can be synchronized to a database table in an instance.
The following links are supported:
- MySQL to MRS Hudi and MySQL to GaussDB(DWS)
- PostgreSQL to GaussDB(DWS)
Figure 4 Database and table shard synchronization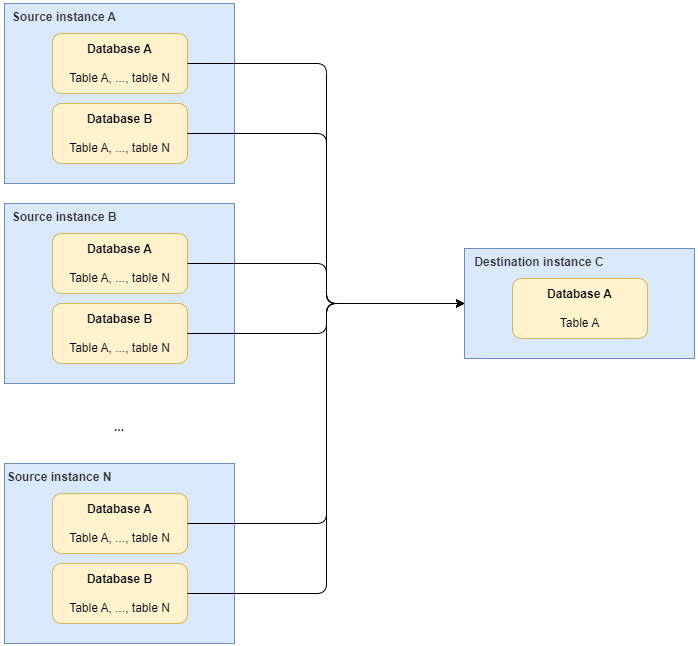
Basic Features
Real-time data migration provides support for big data development and has the following features:
- Timeliness: Data can be synchronized within seconds.
- Reliability: Mechanisms such as recovery upon exceptions and automatic retry ensure data consistency and accuracy.
- Diversity:
- Diverse data sources: Multiple data sources can be selected at the source and destination.
- Diverse scenarios: Some links support full and incremental synchronization, and some links support database and table shards.
- Maintainability: Job monitoring and logs are supported, enabling O&M engineers to locate faults.
- Ease-of-use: You only need to configure necessary information on the console.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






