Does CDM Support Field Conversion?
Yes. CDM supports the following field converters:
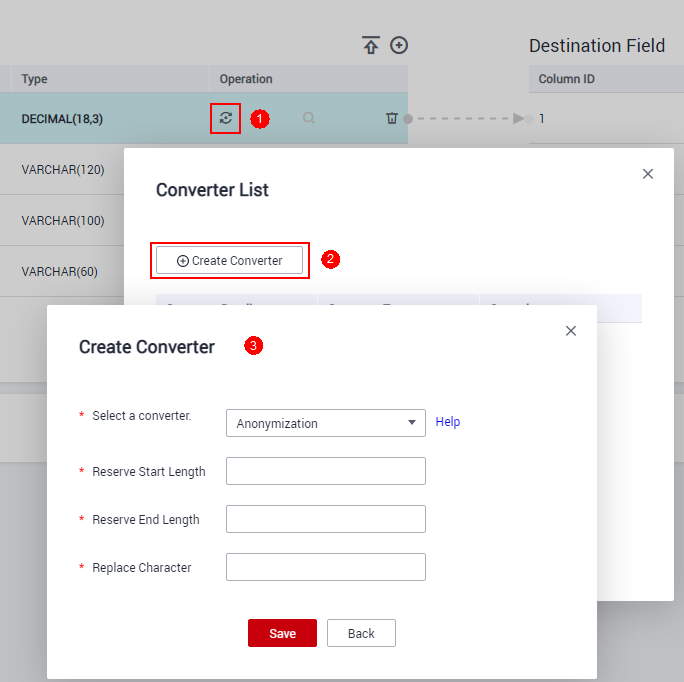
Anonymization
- Set Reserve Start Length to 3.
- Set Reserve End Length to 4.
- Set Replace Character to *.
Trim
This converter is used to automatically delete the spaces before and after a string. No parameters need to be configured.
Reverse String
This converter is used to automatically reverse a string. For example, reverse ABC into CBA. No parameters need to be configured.
Replace String
This converter is used to replace a character string. You need to configure the object to be replaced and the new value.
Expression Conversion
This converter uses the JSP expression language (EL) to convert the current field or a row of data. The JSP EL is used to create arithmetic and logical expressions. In an expression, you can use integers, floating point numbers, strings, constants true and false, and null.
During data conversion, if the content to be replaced contains a special character, use a backslash (\) to escape the special character to a common one.
- The expression supports the following environment variables:
- value: indicates the current field value.
- row: indicates the current row, which is an array type.
- The expression supports the following Utils:
- If the field is of the string type, convert all character strings into lowercase letters, for example, convert aBC to abc.
Expression: StringUtils.lowerCase(value)
- Convert all character strings of the current field to uppercase letters.
- Convert the format of the first date field from 2018-01-05 15:15:05 to 20180105.
Expression: DateUtils.format(DateUtils.parseDate(row[0],"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"),"yyyyMMdd")
- Convert a timestamp to a date string in yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss format, for example, convert 1701312046588 to 2023-11-30 10:40:46.
Expression: DateUtils.format(NumberUtils.toLong(value),"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
- Convert a date string in the yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss format to a timestamp.
Expression: DateUtils.getTime(DateUtils.parseDate(value,"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"))
- If the field value is a date string in yyyy-MM-dd format, extract the year from the field value, for example, extract 2017 from 2017-12-01.
Expression: StringUtils.substringBefore(value,"-")
- If the field value is of the numeric type, convert the value to a new value which is two times greater than the original value:
- Convert the field value true to Y and other field values to N.
Expression: value=="true"?"Y":"N"
- If the field value is of the string type and is left empty, convert it to Default. Otherwise, the field value will not be converted.
Expression: empty value? "Default":value
- Convert date format 2018/01/05 15:15:05 to 2018-01-05 15:15:05:
Expression: DateUtils.format(DateUtils.parseDate(value,"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss"),"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
- Obtain a 36-bit universally unique identifier (UUID):
- If the field is of the string type, capitalize the first letter, for example, convert cat to Cat.
Expression: StringUtils.capitalize(value)
- If the field is of the string type, convert the first letter to a lowercase letter, for example, convert Cat to cat.
Expression: StringUtils.uncapitalize(value)
- If the field is of the string type, use a space to fill in the character string to the specified length and center the character string. If the length of the character string is not shorter than the specified length, do not convert the character string. For example, convert ab to meet the specified length 4.
Expression: StringUtils.center(value,4)
- Delete a newline (including \n, \r, and \r\n) at the end of a character string. For example, convert abc\r\n\r\n to abc\r\n.
Expression: StringUtils.chomp(value)
- If the string contains the specified string, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, abc contains a so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.contains(value,"a")
- If the string contains any character of the specified string, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, zzabyycdxx contains either z or a so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.containsAny(value,"za")
- If the string does not contain any one of the specified characters, true is returned. If any specified character is contained, false is returned. For example, abz contains one character of xyz so that false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.containsNone(value,"xyz")
- If the string contains only the specified characters, true is returned. If any other character is contained, false is returned. For example, abab contains only characters among abc so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.containsOnly(value,"abc")
- If the character string is empty or null, convert it to the specified character string. Otherwise, do not convert the character string. For example, convert the empty character string to null.
- If the string ends with the specified suffix (case sensitive), true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, if the suffix of abcdef is not null, false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.endsWith(value,null)
- If the string is the same as the specified string (case sensitive), true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, after strings abc and ABC are compared, false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.equals(value,"ABC")
- Obtain the first index of the specified character string in a character string. If no index is found, -1 is returned. For example, the first index of ab in aabaabaa is 1.
Expression: StringUtils.indexOf(value,"ab")
- Obtain the last index of the specified character string in a character string. If no index is found, -1 is returned. For example, the last index of k in aFkyk is 4.
Expression: StringUtils.lastIndexOf(value,"k")
- Obtain the first index of the specified character string from the position specified in the character string. If no index is found, -1 is returned. For example, the first index of b obtained after the index 3 of aabaabaa is 5.
Expression: StringUtils.indexOf(value,"b",3)
- Obtain the first index of any specified character in a character string. If no index is found, -1 is returned. For example, the first index of z or a in zzabyycdxx. is 0.
Expression: StringUtils.indexOfAny(value,"za")
- If the string contains any Unicode character, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, ab2c contains only non-Unicode characters so that false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isAlpha(value)
- If the string contains only Unicode characters and digits, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, ab2c contains only Unicode characters and digits, so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isAlphanumeric(value)
- If the string contains only Unicode characters, digits, and spaces, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, ab2c contains only Unicode characters and digits, so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isAlphanumericSpace(value)
- If the string contains only Unicode characters and spaces, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, ab2c contains Unicode characters and digits so that false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isAlphaSpace(value)
- If the string contains only printable ASCII characters, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, for !ab-c~, true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isAsciiPrintable(value)
- If the string is empty or null, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isEmpty(value)
- If the string contains only Unicode digits, true is returned; otherwise, false is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.isNumeric(value)
- Obtain the leftmost characters of the specified length. For example, obtain the leftmost two characters ab from abc.
Expression: StringUtils.left(value,2)
- Obtain the rightmost characters of the specified length. For example, obtain the rightmost two characters bc from abc.
Expression: StringUtils.right(value,2)
- Concatenate the specified character string to the left of the current character string and specify the length of the concatenated character string. If the length of the current character string is not shorter than the specified length, the character string will not be converted. For example, if yz is concatenated to the left of bat and the length must be 8 after concatenation, the character string is yzyzybat after conversion.
Expression: StringUtils.leftPad(value,8,"yz")
- Concatenate the specified character string to the right of the current character string and specify the length of the concatenated character string. If the length of the current character string is not shorter than the specified length, the character string will not be converted. For example, if yz is concatenated to the right of bat and the length must be 8 after concatenation, the character string is batyzyzy after conversion.
Expression: StringUtils.rightPad(value,8,"yz")
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the length of the current character string. If the character string is null, 0 is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.length(value)
- If the field is of the string type, delete all the specified character strings from it. For example, delete ue from queued to obtain qd.
Expression: StringUtils.remove(value,"ue")
- If the field is of the string type, remove the substring at the end of the field. If the specified substring is not at the end of the field, no conversion is performed. For example, remove .com at the end of www.domain.com.
Expression: StringUtils.removeEnd(value,".com")
- If the field is of the string type, delete the substring at the beginning of the field. If the specified substring is not at the beginning of the field, no conversion is performed. For example, delete www. at the beginning of www.domain.com.
Expression: StringUtils.removeStart(value,"www.")
- If the field is of the string type, replace all the specified character strings in the field. For example, replace a in aba with z to obtain zbz.
Expression: StringUtils.replace(value,"a","z")
If the content to be replaced contains a special character, the special character must be escaped to a common character. For example, if you want to delete \t from a string, use the following expression: StringUtils.replace(value,"\\t",""), which means escaping the backslash (\) again.
- If the field is of the string type, replace multiple characters in the character string at a time. For example, replace h in hello with j and o with y to obtain jelly.
Expression: StringUtils.replaceChars(value,"ho","jy")
- If the string starts with the specified prefix (case sensitive), true is returned; otherwise, false is returned. For example, abcdef starts with abc, so that true is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.startsWith(value,"abc")
- If the field is of the string type, delete all the specified characters at the beginning and end of the field. the field. For example, delete all x, y, z, and b from abcyx to obtain abc.
Expression: StringUtils.strip(value,"xyzb")
- If the field is of the string type, delete all the specified characters at the end of the field, for example, delete the "abc" string at the end of the field.
- If the field is of the string type, delete all the specified characters at the beginning of the field, for example, delete all spaces at the beginning of the field.
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring after the specified position (the index starts from 0, including the character at the specified position) of the character string. If the specified position is a negative number, calculate the position in the descending order. The first digit at the end is -1. For example, obtain the character whose index is 2 from abcde (that is, c) and the string after it, that is, cde.
Expression: StringUtils.substring(value,2)
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring in a specified range (the index starts from 0, including the character at the start and excluding the character at the end). If the range is a negative number, calculate the position in the descending order. The first digit at the end is -1. For example, obtain the string between the second character (c) and fourth character (e) of abcde, that is, cd.
Expression: StringUtils.substring(value,2,4)
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring after the first specified character. For example, obtain the substring after the first b in abcba, that is, cba.
Expression: StringUtils.substringAfter(value,"b")
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring after the last specified character. For example, obtain the substring after the last b in abcba, that is, a.
Expression: StringUtils.substringAfterLast(value,"b")
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring before the first specified character. For example, obtain the substring before the first b in abcba, that is, a.
Expression: StringUtils.substringBefore(value,"b")
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring before the last specified character. For example, obtain the substring before the last b in abcba, that is, abc.
Expression: StringUtils.substringBeforeLast(value,"b")
- If the field is of the string type, obtain the substring nested within the specified string. If no substring is found, null is returned. For example, obtain the substring between tag in tagabctag, that is, abc.
Expression: StringUtils.substringBetween(value,"tag")
- If the field is of the string type, delete the control characters (char≤32) at both ends of the character string, for example, delete the spaces at both ends of the character string.
- Convert the character string to a value of the byte type. If the conversion fails, 0 is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toByte(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the byte type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toByte(value,1)
- Convert the character string to a value of the double type. If the conversion fails, 0.0d is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toDouble(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the double type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1.1d, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toDouble(value,1.1d)
- Convert the character string to a value of the float type. If the conversion fails, 0.0f is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toFloat(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the float type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1.1f, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toFloat(value,1.1f)
- Convert the character string to a value of the int type. If the conversion fails, 0 is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toInt(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the int type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toInt(value,1)
- Convert the character string to a value of the long type. If the conversion fails, 0 is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toLong(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the long type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1L, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toLong(value,1L)
- Convert the character string to a value of the short type. If the conversion fails, 0 is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toShort(value)
- Convert the character string to a value of the short type. If the conversion fails, the specified value, for example, 1, is returned.
Expression: NumberUtils.toShort(value,1)
- Convert the IP string to a value of the long type, for example, convert 10.78.124.0 to 172915712.
Expression: CommonUtils.ipToLong(value)
- Read an IP address and physical address mapping file from the network, and download the mapping file to the map collection. url indicates the address for storing the IP mapping file, for example, http://10.114.205.45:21203/sqoop/IpList.csv.
Expression: HttpsUtils.downloadMap("url")
- Cache the IP address and physical address mappings and specify a key for retrieval, for example, ipList.
Expression: CommonUtils.setCache("ipList",HttpsUtils.downloadMap("url"))
- Obtain the cached IP address and physical address mappings.
- Check whether the IP address and physical address mappings are cached.
- Based on the specified offset type (month/day/hour/minute/second) and offset (positive number indicates increase and negative number indicates decrease), convert the time in the specified format to a new time, for example, add 8 hours to 2019-05-21 12:00:00.
Expression: DateUtils.getCurrentTimeByZone("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",value, "hour", 8)
- If the value is empty or null, "aaa" is returned. Otherwise, value is returned.
Expression: StringUtils.defaultIfEmpty(value,"aaa")
- If the field is of the string type, convert all character strings into lowercase letters, for example, convert aBC to abc.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






