ALTER AUDIT POLICY
Description
Modifies the unified audit policy.
Precautions
- Only the user with the POLADMIN or SYSADMIN permission, or initial user has the permission to maintain audit policies.
- The unified audit policy takes effect only after enable_security_policy is set to on.
Syntax
Add or delete an operation type in the audit policy.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY [ IF EXISTS ] policy_name { ADD | REMOVE } { [ privilege_audit_clause ] [ access_audit_clause ] };

Change the filter criteria in the audit policy.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY [ IF EXISTS ] policy_name MODIFY ( filter_group_clause );
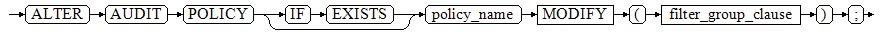
Delete the filter criteria from the audit policy.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY [ IF EXISTS ] policy_name DROP FILTER;
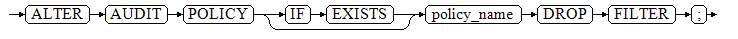
Change the description of the audit policy.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY [ IF EXISTS ] policy_name COMMENTS policy_comments;
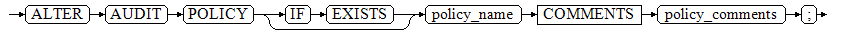
Enable or disable the audit policy.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY [ IF EXISTS ] policy_name { ENABLE | DISABLE };
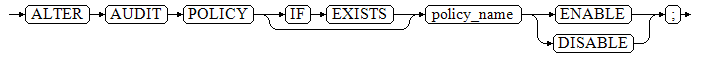
- privilege_audit_clause
DDL operation type and target resource label in the audit policy.
1PRIVILEGES ({ DDL | ALL } [ ON LABEL ( resource_label_name [, ... ] ) ])

- access_audit_clause
DML operation type and target resource label in the audit policy.
ACCESS ({ DML | ALL } [ ON LABEL ( resource_label_name [, ... ] ) ])
- filter_group_clause
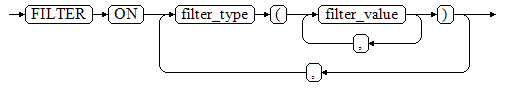
- DDL
- DML
Parameters
- policy_name
Specifies the audit policy name, which must be unique.
Value range: a string. It must comply with the naming convention.
- resource_label_name
Specifies the resource label name.
- DDL
Specifies the operations that are audited in the database: CREATE, ALTER, DROP, ANALYZE, COMMENT, GRANT, REVOKE, SET, and SHOW.
- DML
Specifies the operations that are audited in the database: SELECT, COPY, DEALLOCATE, DELETE, EXECUTE, INSERT, PREPARE, REINDEX, TRUNCATE, and UPDATE.
- ALL
Specifies all operations supported by the specified DDL or DML statements in the database. When the form is { DDL | ALL }, ALL indicates all DDL operations. When the form is { DML | ALL }, ALL indicates all DML operations.
- filter_type
Specifies the types of information to be filtered by the policy: IP, ROLES, and APP.
- filter_value
Specifies the detailed information to be filtered.
- policy_comments
Records description information of the audit policy.
- ENABLE|DISABLE
Enables or disables the unified audit policy.
Examples
- Add or delete an operation type in the audit policy.
-- Create audit policy adt1 for executing CREATE on the database. gaussdb=# CREATE AUDIT POLICY adt1 PRIVILEGES CREATE; -- Add DROP to the adt1 audit policy. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 ADD PRIVILEGES (DROP); -- Delete DROP from the adt1 audit policy. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 REMOVE PRIVILEGES (DROP);
- Change the comments of the audit policy.
-- Change the comment of the adt1 audit policy to adt1_comments. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 COMMENTS 'adt1_comments';
- Change the filter information of the audit policy.
-- Create a user bob_audit. gaussdb=# CREATE USER bob_audit PASSWORD '********'; -- Change the filtering user of the adt1 audit policy to bob_audit. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 MODIFY (FILTER ON (ROLES(bob_audit))); -- Delete user bob_audit. gaussdb=# DROP USER bob_audit;
- Delete the filter criteria from the audit policy.
-- Delete the filter criteria in the adt1 audit policy. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 DROP FILTER; - Disable the audit policy.
-- Disable the adt1 audit policy. gaussdb=# ALTER AUDIT POLICY adt1 DISABLE; -- Delete the adt1 audit policy. gaussdb=# DROP AUDIT POLICY adt1;
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






