Overview
Scenario
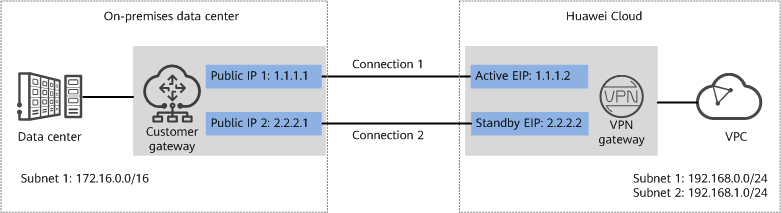
To meet service requirements, enterprise A needs to implement communication between its on-premises data center and a VPC on the cloud. For reliability purposes, enterprise A requires that its on-premises data center use two public IP addresses to connect to the VPN gateway on the cloud.
Networking
Figure 1 shows the networking where the VPN service is used to connect the on-premises data center to the VPC.
Solution Advantages
- A VPN gateway provides two EIPs to establish dual independent VPN connections with a customer gateway. If one VPN connection fails, traffic can be quickly switched to the other VPN connection, ensuring reliability.
- Active-active VPN gateways can be deployed in different AZs to ensure AZ-level high availability.
Limitations and Constraints
- The local and customer subnets of the VPN gateway cannot be the same. That is, the VPC subnet and the data center subnet to be interconnected cannot be the same.
- The IKE policy, IPsec policy, and PSK of the VPN gateway must be the same as those of the customer gateway.
- The local and remote interface address configurations on the VPN gateway and customer gateway are reversed.
- The security groups associated with ECSs in the VPC permit access from and to the on-premises data center.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.