Using a VPC Peering Connection to Connect ECSs in Two VPCs
You can configure a VPC peering connection and set the destination of the routes added to VPC route tables to the private IP address of ECS in the peer VPC. In this way, the two ECS are connected.
|
Scenario |
Scenario Description |
IP Address Version |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ECS in a central VPC peered to ECSs in two other VPCs |
You want a central VPC to communicate with the other two VPCs. However, you do not want the other two VPCs to communicate with each other. The other two VPCs have the same CIDR block and also include subnets that overlap. To prevent route conflicts in the central VPC, you can configure VPC peering connections to connect to specific ECSs in the other two VPCs. |
IPv4 |
ECS in a Central VPC Peered to ECSs in Two Other VPCs (IPv4) |
|
A central VPC peered with two other VPCs using longest prefix match |
This scenario is similar to the preceding one. In addition to peering specific ECSs, you can create the following VPC peering connections based on the longest prefix match rule:
This configuration expands the communication scope. |
IPv4 |
A Central VPC Peered with Two Other VPCs Using Longest Prefix Match (IPv4) |
ECS in a Central VPC Peered to ECSs in Two Other VPCs (IPv4)
You want to create a VPC peering connection between VPC-A and VPC-B, and between VPC-A and VPC-C. VPC-B and VPC-C have matching CIDR blocks. You can set the destinations of routes to private IP addresses of specific ECSs to limit traffic to these ECSs. If the destination of a route is not properly planned, traffic cannot be correctly forwarded. For details, see One Central VPC Peered to Overlapping Subnets from Two VPCs (IPv4).

|
VPC Name |
VPC CIDR Block |
Subnet Name |
Subnet CIDR Block |
VPC Route Table |
ECS Name |
Security Group |
Private IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC-A |
172.16.0.0/16 |
Subnet-A01 |
172.16.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-A |
ECS-A01-1 |
sg-web: general-purpose web server |
172.16.0.111 |
|
ECS-A01-2 |
172.16.0.218 |
||||||
|
VPC-B |
10.0.0.0/16 |
Subnet-B01 |
10.0.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-B |
ECS-B01 |
10.0.0.139 |
|
|
VPC-C |
10.0.0.0/16 |
Subnet-C01 |
10.0.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-C |
ECS-C01 |
10.0.0.71 |
|
Peering Relationship |
Peering Connection Name |
Local VPC |
Peer VPC |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ECS-A01-1 in VPC-A is peered with ECS-B01 in VPC-B. |
Peering-AB |
VPC-A |
VPC-B |
|
ECS-A01-2 in VPC-A is peered with ECS-C01 in VPC-C. |
Peering-AC |
VPC-A |
VPC-C |
After the VPC peering connections are created, add the following routes to the route tables of the local and peer VPCs:
|
Route Table |
Destination |
Next Hop |
Route Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rtb-VPC-A |
172.16.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
10.0.0.139/32 (ECS-B01) |
Peering-AB |
Custom |
Add a route with the private IP address of ECS-B01 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
|
|
10.0.0.71/32 (ECS-C01) |
Peering-AC |
Custom |
Add a route with the private IP address of ECS-C01 as the destination and Peering-AC as the next hop. |
|
|
rtb-VPC-B |
10.0.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
172.16.0.111/32 (ECS-A01-1) |
Peering-AB |
Custom |
Add a route with the private IP address of ECS-A01-1 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
|
|
rtb-VPC-C |
10.0.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
172.16.0.218/32 (ECS-A01-2) |
Peering-AC |
Custom |
Add a route with the private IP address of ECS-A01-2 as the destination and Peering-AC as the next hop. |
A Central VPC Peered with Two Other VPCs Using Longest Prefix Match (IPv4)
You want to create a VPC peering connection between VPC-A and VPC-B, and between VPC-A and VPC-C. VPC-B and VPC-C have matching CIDR blocks. You can set the destinations of routes to private IP addresses of specific ECSs to limit traffic to these ECSs. If the destination of a route is not properly planned, traffic cannot be correctly forwarded. For details, see One Central VPC Peered to Overlapping Subnets from Two VPCs (IPv4).
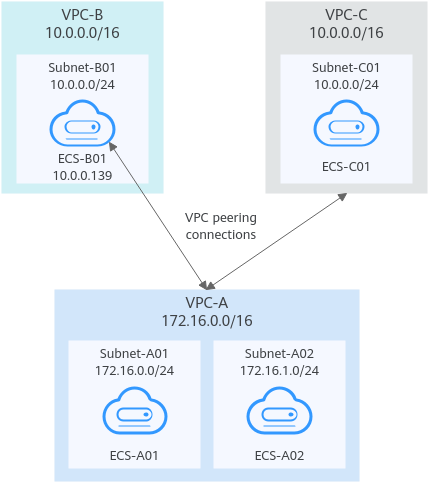
|
VPC Name |
VPC CIDR Block |
Subnet Name |
Subnet CIDR Block |
VPC Route Table |
ECS Name |
Security Group |
Private IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC-A |
172.16.0.0/16 |
Subnet-A01 |
172.16.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-A |
ECS-A01 |
sg-web: general-purpose web server |
172.16.0.111 |
|
Subnet-A02 |
172.16.1.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-A |
ECS-A02 |
172.16.1.91 |
|||
|
VPC-B |
10.0.0.0/16 |
Subnet-B01 |
10.0.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-B |
ECS-B01 |
10.0.0.139 |
|
|
VPC-C |
10.0.0.0/16 |
Subnet-C01 |
10.0.0.0/24 |
rtb-VPC-C |
ECS-C01 |
10.0.0.71 |
|
Peering Relationship |
Peering Connection Name |
Local VPC |
Peer VPC |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC-A is peered with ECS-B01 in VPC-B. |
Peering-AB |
VPC-A |
VPC-B |
|
VPC-A is peered with VPC-C. |
Peering-AC |
VPC-A |
VPC-C |
After the VPC peering connections are created, add the following routes to the route tables of the local and peer VPCs:
|
Route Table |
Destination |
Next Hop |
Route Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rtb-VPC-A |
172.16.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
172.16.1.0/24 |
Local |
System |
||
|
10.0.0.139/32 (ECS-B01) |
Peering-AB |
Custom |
Add a route with the private IP address of ECS-B01 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
|
|
10.0.0.0/16 (VPC-C) |
Peering-AC |
Custom |
Add a route with the CIDR block of VPC-C as the destination and Peering-AC as the next hop. |
|
|
rtb-VPC-B |
10.0.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
172.16.0.0/16 (VPC-A) |
Peering-AB |
Custom |
Add a route with the CIDR block of VPC-A as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
|
|
rtb-VPC-C |
10.0.0.0/24 |
Local |
System |
Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. |
|
172.16.0.0/16 (VPC-A) |
Peering-AC |
Custom |
Add a route with the CIDR block of VPC-A as the destination and Peering-AC as the next hop. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






