Overview
Application Scenario
As big data technologies burgeon, people are deepening their understanding of data values. Big data is everywhere in a variety of industries. According to a report, of all enterprises around the world, over 39.6% have applied big data to their businesses and earned benefits, more than 89.6% already have or plan to set up departments for big data analysis, and over 60% are investing more in big data. The capability of leveraging big data is crucial to each industry's success in the future.
In big data scenarios, data is a new asset, and intelligence has become a new productivity. Enterprises are in urgent need of digital transformation to improve productivity and to maximize the data value. Before services are migrated to the cloud, traditional enterprises deploy their services and store data in multiple clusters in the on-premises IDC, and one server provides both compute and storage capabilities. This causes key problems shown in Table 1, and these problems have hindered the enterprise's digital transformation.
|
No. |
Key Concern |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Hard to share data among multiple clusters |
Enterprise's data is stored in multiple clusters, resulting in the following problems:
|
|
2 |
Resource waste due to coupled compute and storage resources |
Compute and storage resources must be expanded proportionally even if their demands are inconsistent, which causes a waste of resources. |
|
3 |
Low utilization and high cost due to three copies of data |
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) stores data in three copies. The disk space utilization is only 33%, and the utilization of a single disk is lower than 70%. |
Solution Architecture
To address the problems in the table above, Huawei Cloud provides a solution with decoupled storage and compute, where OBS is used as the unified data lake storage.
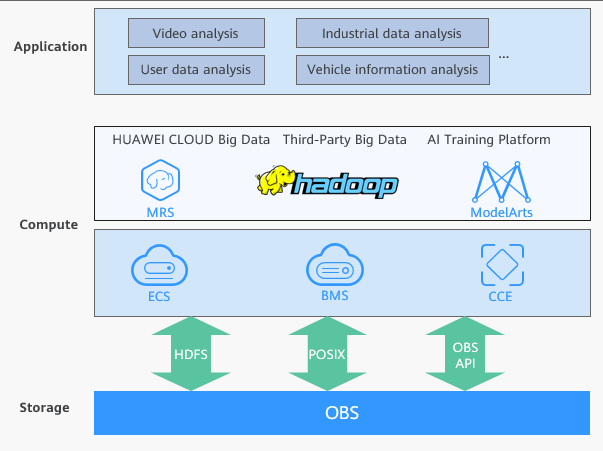
Relying on the large capacity and high bandwidth of OBS and shared access based on multiple protocols (HDFS, POSIX, and OBS API), this solution enables Hadoop compute engines (such as Hive and Spark) compatible with each other.
Solution Advantages
Compared with traditional solutions, this solution has the advantages described in Table 2.
|
No. |
Advantage |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Converged, efficient, and collaborative analysis |
|
|
2 |
High resource utilization thanks to decoupled storage and compute |
Compute and storage resources can be separately scaled. This improves the resource utilization. |
|
3 |
High utilization and low cost with EC storage |
OBS supports Erasure Code (EC), the most utilized distributed fault tolerance technology. EC greatly increases the disk space utilization and requires much less storage space than the three copies of data mechanism. |
In addition, OBS provides the OBSFileSystem plug-in (OBSA-HDFS) to seamlessly connect to the upper-layer big data platform, requiring no modifications.
OBSFileSystem provides HDFS-related APIs so that big data compute engines (such as Hive and Spark) can use OBS as the underlying storage.
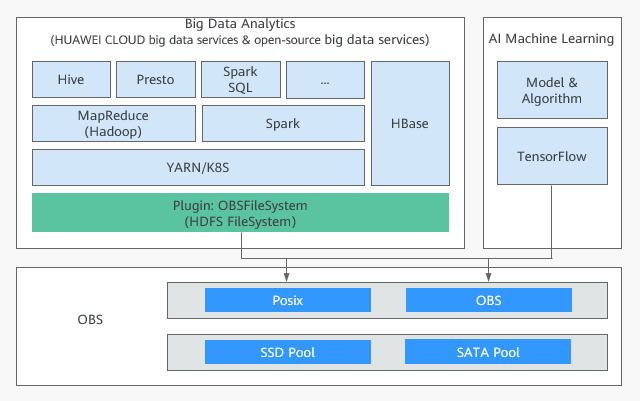
OBS offers object storage buckets (object semantics) and parallel file systems (POSIX). In big data scenarios, parallel file systems are recommended. Parallel file systems support POSIX and are encapsulated through OBSFileSystem. Compared with object semantics, parallel file systems have additional APIs (including Rename, Append, hflush, and hsync). These APIs supplement HDFS semantics and provide better performance for big data computing.
Based on the preceding advantages, compared with traditional big data solutions, the Huawei Cloud big data solution with decoupled storage and compute requires significantly fewer compute resources, storage resources, and servers for the same service scale. This greatly increases resource utilization and reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Application Scope
This practice explains how to connect different big data platforms and components to OBS in the big data solutions with decoupled storage and compute, and how to migrate data from HDFS to OBS.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






