Recording the Time When Data Is Written to the Database
When you create a job on the CDM console to migrate tables or files of a relational database, you can add a field to record the time when they were written to the database.
Prerequisites
- A link has been created, and the source end of the connector is a relational database.
- The destination data table contains a date and time field or timestamp field. In the automatic table creation scenario, you need to manually create the date and time field or timestamp field in the destination table in advance.
Creating a Table/File Migration Job
- Create a table/file migration job, and select the created source connector and destination connector.
Figure 1 Configuring the job
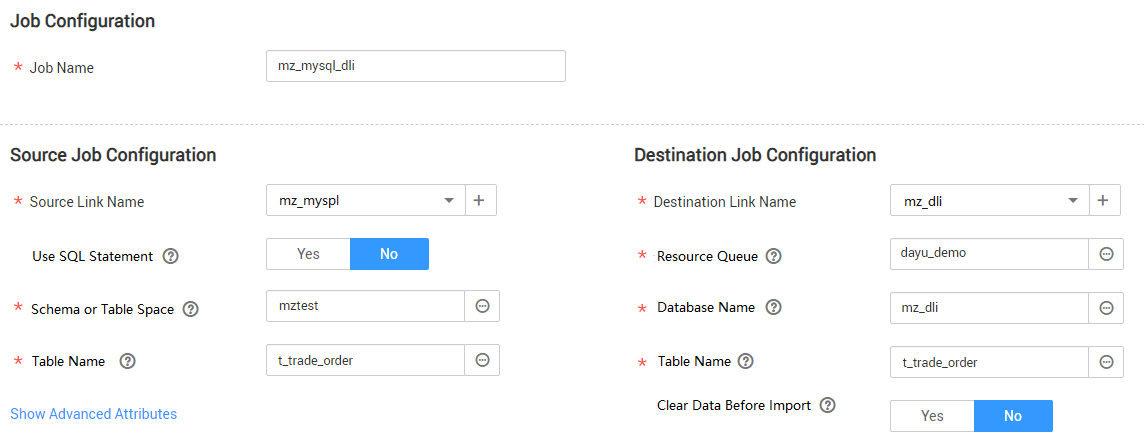
- Click Next to go to the Map Field page and click
 .
Figure 2 Configuring field mapping
.
Figure 2 Configuring field mapping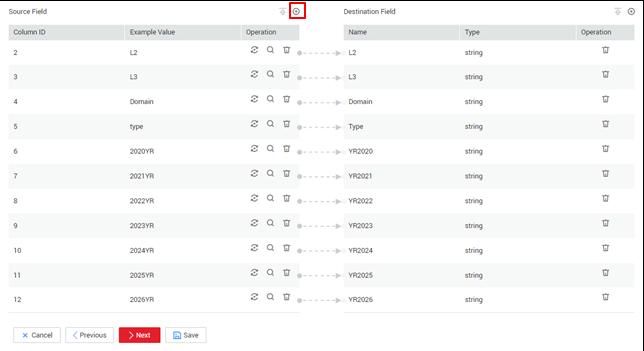
- Click the Custom Fields tab, set the field name and value, and click OK.
Name: Enter InputTime.
Value: Enter ${timestamp()}. For more time macro variables, see Table 1.Figure 3 Add Field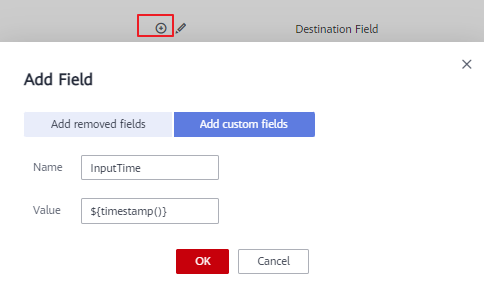
Table 1 Macro variable definition of time and date Macro Variable
Description
Display Effect
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd)}
Returns the current date in yyyy-MM-dd format.
2017-10-16
${dateformat(yyyy/MM/dd)}
Returns the current date in yyyy/MM/dd format.
2017/10/16
${dateformat(yyyy_MM_dd HH:mm:ss)}
Returns the current time in yyyy_MM_dd HH:mm:ss format.
2017_10_16 09:00:00
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss, -1, DAY)}
Returns the current time in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format. The date is one day before the current day.
2017-10-15 09:00:00
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd, -1, DAY)} 00:00:00
Returns 00:00:00 of the day before the current day in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format.
2017-10-15 00:00:00
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd, -1, DAY)} 12:00:00
Returns 12:00:00 of the day before the current day in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format.
2017-10-15 12:00:00
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd, -N, DAY)} 00:00:00
Returns 00:00:00 of the day N days before the current day in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format.
When N is 3:
2017-10-13 00:00:00
${dateformat(yyyy-MM-dd, -N, DAY)} 12:00:00
Returns 12:00:00 of the day N days before the current day in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format.
When N is 3:
2017-10-13 12:00:00
${timestamp()}
Returns the timestamp of the current time, that is, the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since 00:00:00 on January 1, 1970.
1508115600000
${timestamp(-10, MINUTE)}
Returns the timestamp generated 10 minutes before the current time point.
1508115000000
${timestamp(dateformat(yyyyMMdd))}
Returns the timestamp of 00:00:00 of the current day.
1508083200000
${timestamp(dateformat(yyyyMMdd,-1,DAY))}
Returns the timestamp of 00:00:00 of the previous day.
1507996800000
${timestamp(dateformat(yyyyMMddHH))}
Returns the timestamp of the current hour.
1508115600000
- After a field is added, its sample value is not displayed on the console. This does not affect the field value transmission. CDM directly writes the field value to the destination end.
- The Custom Fields tab is available only when the source connector is JDBC, HBase, MongoDB, Elasticsearch, or Kafka, or the destination connector is HBase.
- After adding the fields, ensure that the customized import time field matches the field type of the destination table.
- Click Next and set task parameters. Generally, retain the default values of all parameters.
- Click Save and Run. On the Table/File Migration page, you can view the job execution progress and result.
- After the job is successfully executed, in the Operation column of the job, click Historical Record to view the job's historical execution records and read/write statistics.
On the Historical Record page, click Log to view the job logs.
- Go to the destination data source to check the time when the data is imported to the database.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






